
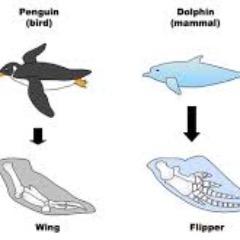
The same relationship between complexity and shared evolutionary history is true for homologous structures in organisms. However, if two people both invented a hammer, it would be reasonable to conclude that both could have the original idea without the help of the other. Imagine two people from different countries both inventing a car with all the same parts and in exactly the same arrangement without any previous or shared knowledge. The more complex the feature, the more likely any kind of overlap is due to a common evolutionary past. Notice it is not simply a single bone, but rather a grouping of several bones arranged in a similar way. (credit a: modification of work by Steve Hillebrand, USFWS credit b: modification of work by U.S.
Bat and bird wings are homologous structures, indicating that bats and birds share a common evolutionary past. Predator-prey "arms race"Predators evolve better ways to catch prey.Figure 1.

Organisms that are NOT related evolve similar traits as a result of evolving to fit into similar environments or ecological niches.They have the same function and shape, but are made differently.Īnalagous structures help to show Convergent Evolution The wings of the bat, butterfly, and bird are made of different coverings, and insects do not have internal bones.

The bones of the bat, mouse, and human are homologous.

Homologous Structures (flowers)Broccoli and Cauliflower evolved from Mustard


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
